Preparing RHOCP for RHOSP Network Isolation
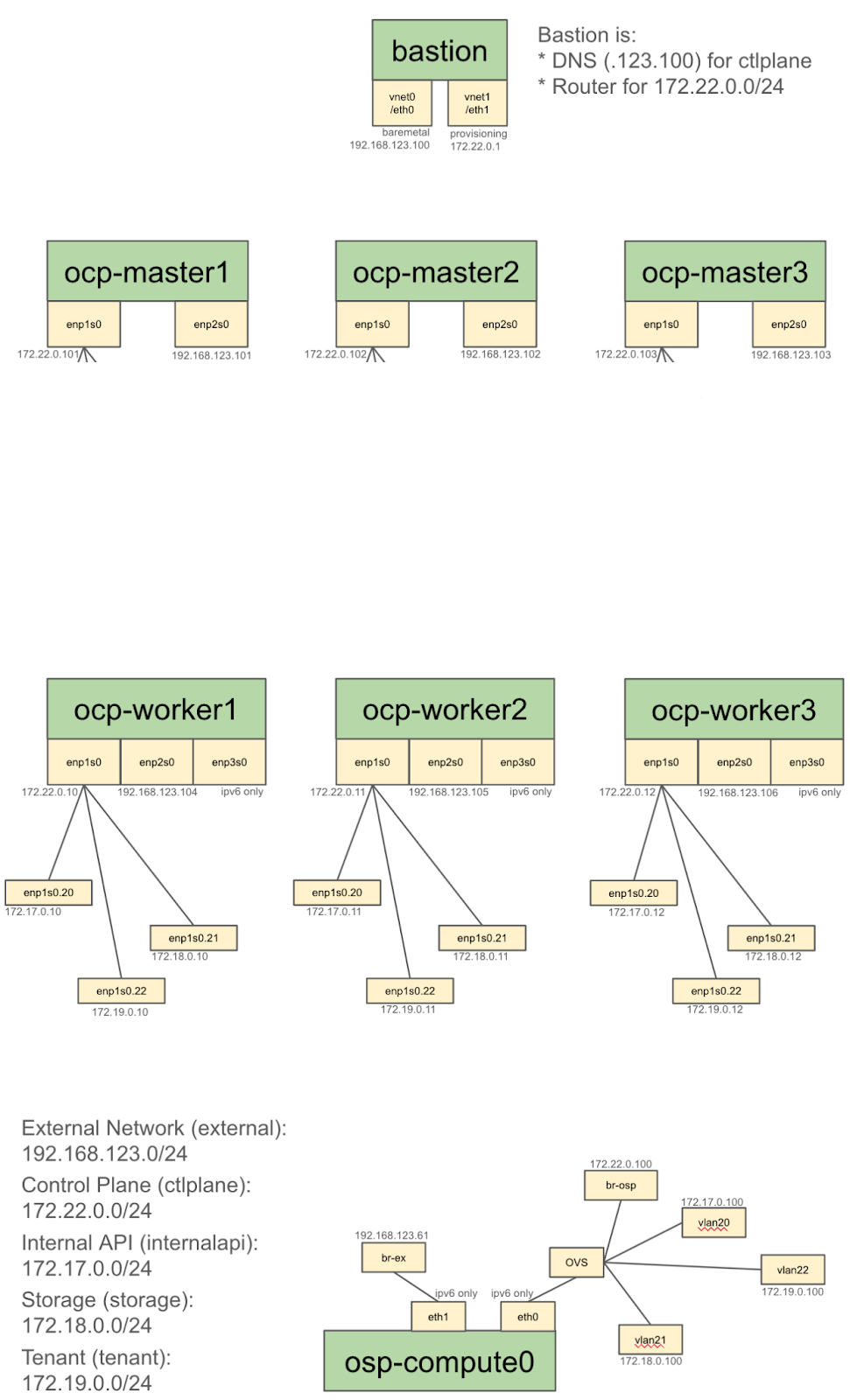
The following diagrams shows the network topology of the lab environment:
Using ArgoCD application to install configure networking
Create an argocd application manifest to deploy the networking configuration:
cat << EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: network-configuration
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: 'https://github.com/rh-osp-demo/showroom_osp-on-ocp.git'
targetRevision: HEAD
path: content/files/manifests/network-configuration
destination:
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
namespace: default
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: false
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
EOFAccess the OpenShift Gitops console to check the deployment of the network configuration.
If your cluster is RHOCP 4.14 or later and it has OVNKubernetes as the network back end, then you must enable global forwarding so that MetalLB can work on a secondary network interface.
Check the network back end used by your cluster:
oc get network.operator cluster --output=jsonpath='{.spec.defaultNetwork.type}'If the back end is OVNKubernetes, then run the following command to enable global IP forwarding:
oc patch network.operator cluster -p '{"spec":{"defaultNetwork":{"ovnKubernetesConfig":{"gatewayConfig":{"ipForwarding": "Global"}}}}}' --type=mergeNodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy (nncp) resource is used to configure RHOSO openstack services network isolation:
oc get nncpNAME STATUS REASON
osp-enp1s0-worker-ocp4-worker1 Available SuccessfullyConfigured
osp-enp1s0-worker-ocp4-worker2 Available SuccessfullyConfigured
osp-enp1s0-worker-ocp4-worker3 Available SuccessfullyConfiguredYou can describe the NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicy applied in worker using osp-enp1s0-worker-ocp4-worker1:
oc describe nncp osp-enp1s0-worker-ocp4-worker1[...]
Spec:
Desired State:
Interfaces:
Description: internalapi vlan interface
ipv4:
Address:
Ip: 172.17.0.10
Prefix - Length: 24
Dhcp: false
Enabled: true
ipv6:
Enabled: false
Name: enp1s0.20
State: up
Type: vlan
Vlan:
Base - Iface: enp1s0
Id: 20
Description: storage vlan interface
ipv4:
Address:
Ip: 172.18.0.10
Prefix - Length: 24
Dhcp: false
Enabled: true
ipv6:
Enabled: false
Name: enp1s0.21
State: up
Type: vlan
Vlan:
Base - Iface: enp1s0
Id: 21
Description: tenant vlan interface
ipv4:
Address:
Ip: 172.19.0.10
Prefix - Length: 24
Dhcp: false
Enabled: true
ipv6:
Enabled: false
Name: enp1s0.22
State: up
Type: vlan
Vlan:
Base - Iface: enp1s0
Id: 22
Description: Configuring enp1s0
ipv4:
Address:
Ip: 172.22.0.10
Prefix - Length: 24
Dhcp: false
Enabled: true
ipv6:
Enabled: false
Mtu: 1500
Name: enp1s0
State: up
Type: ethernet
Node Selector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: ocp4-worker1.aio.example.com
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker:
[...]Review the NetworkAttachmentDefinition (nad) resources for each isolated network to attach a service pod to the corresponding network:
oc get Network-Attachment-Definitions -n openstackNAME AGE
ctlplane 4h47m
external 4h47m
internalapi 4h47m
storage 4h47m
tenant 4h47mReview the internalapi nad IP addressing configuration:
oc describe Network-Attachment-Definitions internalapi -n openstackName: internalapi
Namespace: openstack
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/instance=network-configuration
Annotations: argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: 1
API Version: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1
Kind: NetworkAttachmentDefinition
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2024-07-15T10:16:55Z
Generation: 1
Managed Fields:
API Version: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1
Fields Type: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.:
f:argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave:
f:kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
f:labels:
.:
f:app.kubernetes.io/instance:
f:spec:
.:
f:config:
Manager: argocd-controller
Operation: Update
Time: 2024-07-15T10:16:55Z
Resource Version: 81104
UID: c160968d-dec2-46a2-b147-6e3eb1b9040c
Spec:
Config: {
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"name": "internalapi",
"type": "macvlan",
"master": "enp1s0.20",
"ipam": {
"type": "whereabouts",
"range": "172.17.0.0/24",
"range_start": "172.17.0.30",
"range_end": "172.17.0.70"
}
}
Events: <none>Review the MetalLB IP address range. You use the MetalLB Operator to expose internal service endpoints on the isolated networks. By default, the public service endpoints are exposed as RHOCP routes.:
oc get IPAddressPools -n metallb-systemNAME AUTO ASSIGN AVOID BUGGY IPS ADDRESSES
ctlplane true false ["172.22.0.80-172.22.0.90"]
internalapi true false ["172.17.0.80-172.17.0.90"]
storage true false ["172.18.0.80-172.18.0.90"]
tenant true false ["172.19.0.80-172.19.0.90"]Review the L2Advertisement resource which will define which node advertises a service to the local network which has been preconfigured for your demo environment:
oc get L2Advertisements -n metallb-systemNAME IPADDRESSPOOLS IPADDRESSPOOL SELECTORS INTERFACES
ctlplane ["ctlplane"] ["enp1s0"]
internalapi ["internalapi"] ["enp1s0.20"]
storage ["storage"] ["enp1s0.21"]
tenant ["tenant"] ["enp1s0.22"]Finally, review the data plane network. A NetConfig custom resource (CR) is used to configure all the subnets for the data plane networks. You must define at least one control plane network for your data plane. You can also define VLAN networks to create network isolation for composable networks, such as InternalAPI, Storage, and External. Each network definition must include the IP address assignment:
oc get netconfigs -n openstackNAME AGE
openstacknetconfig 4h49moc describe netconfig openstacknetconfig -n openstack[...]
Spec:
Networks:
Dns Domain: ctlplane.aio.example.com
Mtu: 1500
Name: ctlplane
Subnets:
Allocation Ranges:
End: 172.22.0.120
Start: 172.22.0.100
End: 172.22.0.200
Start: 172.22.0.150
Cidr: 172.22.0.0/24
Gateway: 172.22.0.1
Name: subnet1
Dns Domain: internalapi.aio.example.com
Mtu: 1500
Name: internalapi
Subnets:
Allocation Ranges:
End: 172.17.0.250
Start: 172.17.0.100
Cidr: 172.17.0.0/24
Exclude Addresses:
172.17.0.10
172.17.0.12
Name: subnet1
Vlan: 20
Dns Domain: tenant.aio.example.com
Mtu: 1500
Name: tenant
Subnets:
Allocation Ranges:
End: 172.19.0.250
Start: 172.19.0.100
Cidr: 172.19.0.0/24
Exclude Addresses:
172.19.0.10
172.19.0.12
Name: subnet1
Vlan: 22
Dns Domain: storage.aio.example.com
Mtu: 1500
Name: storage
Subnets:
Allocation Ranges:
End: 172.18.0.250
Start: 172.18.0.100
Cidr: 172.18.0.0/24
Exclude Addresses:
172.18.0.10
172.18.0.12
Name: subnet1
Vlan: 21
Dns Domain: external.aio.example.com
Mtu: 1500
Name: external
Subnets:
Allocation Ranges:
End: 192.168.123.90
Start: 192.168.123.61
Cidr: 192.168.123.0/24
Gateway: 192.168.123.1
Name: subnet1
[...]